His highly influential book entitled Experiential Learning. Virtual Patient Cases for Active Student Participation in Nursing Education Students Learning Experiences.
Kolb S Learning Styles And Experiential Learning Model
Experiential Learning Kolb 14 years ago Humanist Theories Learning Theories Models 0 A four-stage cyclical theory of learning Kolbs experiential learning theory is a holistic perspective that combines experience perception cognition and behavior.
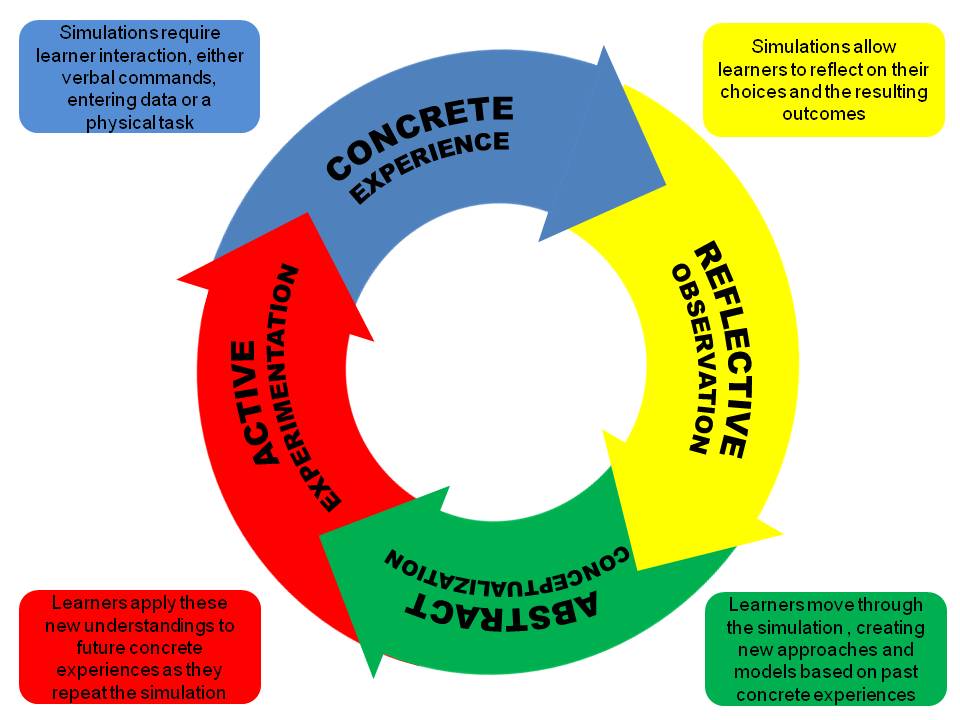
Kolb 1984 experiential learning reference. Learning is a process whereby knowledge is created through transformation of experience Kolb 1984 p38 David A. Exploring the Experiences of Nursing Students during Debriefing. A four stage cycle of learning and four separate learning styles.
Experience as the Source of Learning and Development Englewood Cliffs NJ. Kolbs experiential learning theory works on two levels. Kolbs 1984 learning cycle.
B Observation and reflection. Many of us engaged in professional learning have a broad understanding of the work of David Kolb. Experience as the Source of Learning and Development on the works of John Dewey Jean Piaget Carl Jung Kurt Lewin and William James.
Collection of materials by Kolb and others well worth exploring. In 1984 David A. Kolb based his book Experiential Learning.
Experience as the source of learning and development was first published in 1984 since when his ideas have had a dramatic impact on the design and development of lifelong learning models. Experiential Learning Theory Bibliography. Thinking about these experiences.
Experience as the source of learning and development Englewood Cliffs Prentice Hall 1984. Unpublished thesis PhD University of Limerick. This book essentially exposed the principle that a person would learn through discovery and experience.
Kolbs experiential learning theory ELT is a learning theory developed by David A. Kolb first proposed his 4-stage theory of experiential learning in a book published in 1984. The full reference for this book is provided below and should be placed in the reference list of any reflective report.
Prepared by Alice Kolb and David Kolb this is an extensive bibliography of on experiential learning theory from 1971-2001. 1980 Ursprung auf 1971 Experiential Learning Kolb 1984 Ursprung ebenfalls 1971 sowie Transformative Learning Mezirow 1990 Ursprung auf 1978. David Kolb published his learning styles model in 1984 from which he developed his learning style inventory.
An investigation into the application of the tool with particular reference to its relevance to problem solving and the use of scientific language. David Kolb published his learning styles model in 1984 from which he developed his learning style inventory. Experience as the Source of Learning and Development Vol.
David Kolbs learning cycle allows you to structure a piece of reflective writing around four distinct stages. Experience as the source of learning and development Vol. Kolb believed that ideally learners progressed through the stages to complete a cycle and as a result transformed their experiences into knowledge.
Much of Kolbs theory is concerned with the learners internal cognitive processes. A theory developed by psychologist David Kolb that describes how four stages influence the way that people learn. Knowledge results from the combination of grasping and transforming experience Kolb 1984.
Wafaa Elarousy 1 2 Jennifer de Beer 1 Hend Alnajjar 1. Experiential Learning Theory ELT David Kolb 1984 This theory defines learning as the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience. Being involved in the world.
Kolb published a ground breaking book entitled Experiential Learning. Here weve labelled them as. Experience as the source of learning and development.
The Reference Paper on on Reflective Teaching. Englewood Cliffs NJ Prentice Hall. Experience reflect conceptualise and apply.
Drawing conclusions from these experiences and making generalizationsthereby constructing new theories or building on. Experienced Based Learning Systems Research Library. Kolb who published his model in 1984He was inspired by the work of Kurt Lewin who was a gestalt psychologist in BerlinELT is a method where a persons skills and job requirements can be assessed in the same language that its commensurability can be measured.
The first is that learning follows a four-stage cycle as outlined below. Has been cited by the following article. There are two parts to Kolbs Experiential Learning Theory.
Has been cited by the following article. Experience In the first stage of this cycle think about and then write down the situation you are. Kolbs experiential learning theory works on two levels.
A four-stage cycle of learning and four separate learning styles. Much of Kolbs theory is concerned with the learners internal cognitive processes. What is Experiential Learning.
Experiential Learning Experience as the Source of Learning and Development. Kolbs experiential learning theory works on two. Between this technique and the others is that the first and second stages of Kolbs Experiential Learning Theory are led by the students concrete experience reflective.
On each of the 16 scenario questions you check one or more boxes that best represent your reaction to the scenario. This Learning Styles Quiz is copyrighted by The Center for New Discoveries in Learning Inc.
 Learning Styles Questionnaires And Instruments
Learning Styles Questionnaires And Instruments
They can tick more than one box if applicable.

Simple learning styles questionnaire. VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire Circle or tick the answer that most represents how you generally behave. A Hear someone tell me how. Learning Styles Questionnaire Directions.
The modality learning channel preference questionnaire reproduced here is by OBrien 1985. I learn by hearing my own voice on tape. The LSQ Learning Style Questionnaire is a self-administered questionnaire determines your preferred learning style.
Please click more than one if a single answer does not match your perception. This quiz will help you find your dominant learning style. Learning Styles Inventory LSI Yes No 1.
VARK Questionnaire version 801. V Watch someone show me how. A highly cost-effective self-development instrument the Learning Styles Questionnaire LSQ is designed to measure learning preferences in individuals aged 16.
More information is coming soon so return often to check for updates. Complete the table below by assigning the following point values for each question. Most people learn in all three ways just to varying degrees.
Understanding Visual Auditory and Kinesthetic Learning Styles. Knowing your learning style can accelerate your learning as you undertake activities that best fit your preferred style. Adapt Your Studying Techniques to Your Learning Style.
Learning Style Inventory Directions. Circle the letter before the statement that best describes you. Please respond to all.
Visual auditory and kinesthetic are the three basic type of learning style. When I read I often find that I. You can do the test now.
Statements Choice A Choice B Choice C 1. 0 - the statement is nothing like me 1 - the statement is partially like me 2 - the statement is very much like me. The LSQ is based on David Kolbs Learning Cycle theory which looks directly at how individuals learn rather than their tendencies to learn.
Answer each statement in the following manner. Activities and Ideas for Students with an Auditory Learning Style. When I operate new equipment I generally.
Often 5 points Sometimes 3 points Seldom 1 point Then add the points in each column to obtain your learning preference score under each. Learning Styles Questionnaire If you understand your preferred learning style then youll make it easier to seek out materials and resources in a format that suits you best. Learning styles impact how we process information and how we communicate information to others.
Kolbs Learning Style Questionnaire This questionnaire is designed to find out your preferred learning styless as an adult. Now that you are aware of your own learning style you can begin to select learning strategies that work with your strengths. Questions Per Page Page.
Below is a free VAK Visual Auditory and Kinaesthetic learning styles questionnaire for you to take. Memletics Learning Styles Questionnaire. Read the statements to the children and ask them to tick the box that is most like them.
To complete read each sentence carefully and consider if it applies to you. Choose the answer which best explains your preference and click the box next to it. You understand and remember things by sight.
K Try to do it myself. The learning styles inventory quiz questionnaire test is free and available on this site. I like to listen and discuss work with a partner.
A read the instructions first. You can picture what you are learning in your head and you learn best by using methods that are primarily visual. I prefer to learn something new by reading about it.
How to Tell If You Are Right-Brain Dominant. As a visual learner you are usually neat and clean. You like to see what you are learning.
If you are a visual learner you learn by reading or seeing pictures. On the line in front of each statement indicate how often the sentence applies to you according to the chart below. The VARK Questionnaire includes four learning styles - visual auralauditory readingwriting and kinesthetic.
Take the free Learning Styles Quiz now to find out how to maximize your learning and improve your life. Learning Style Questionnaire University of California Merced Student Advising and Learning Center. You can press tab to go to the next question.
When youre finished click OK and youll instantly get your results. Note that you should only use styles inventories as a general guide to your styles - not as an absolute answer. Over the years you have probably developed learning habits that help you benefit more from some experiences than from others.
Its best to complete the questionnaire before reading the accompanying explanation 1. Holistic or Global Learning. If I have to learn how to do something I learn best when I.
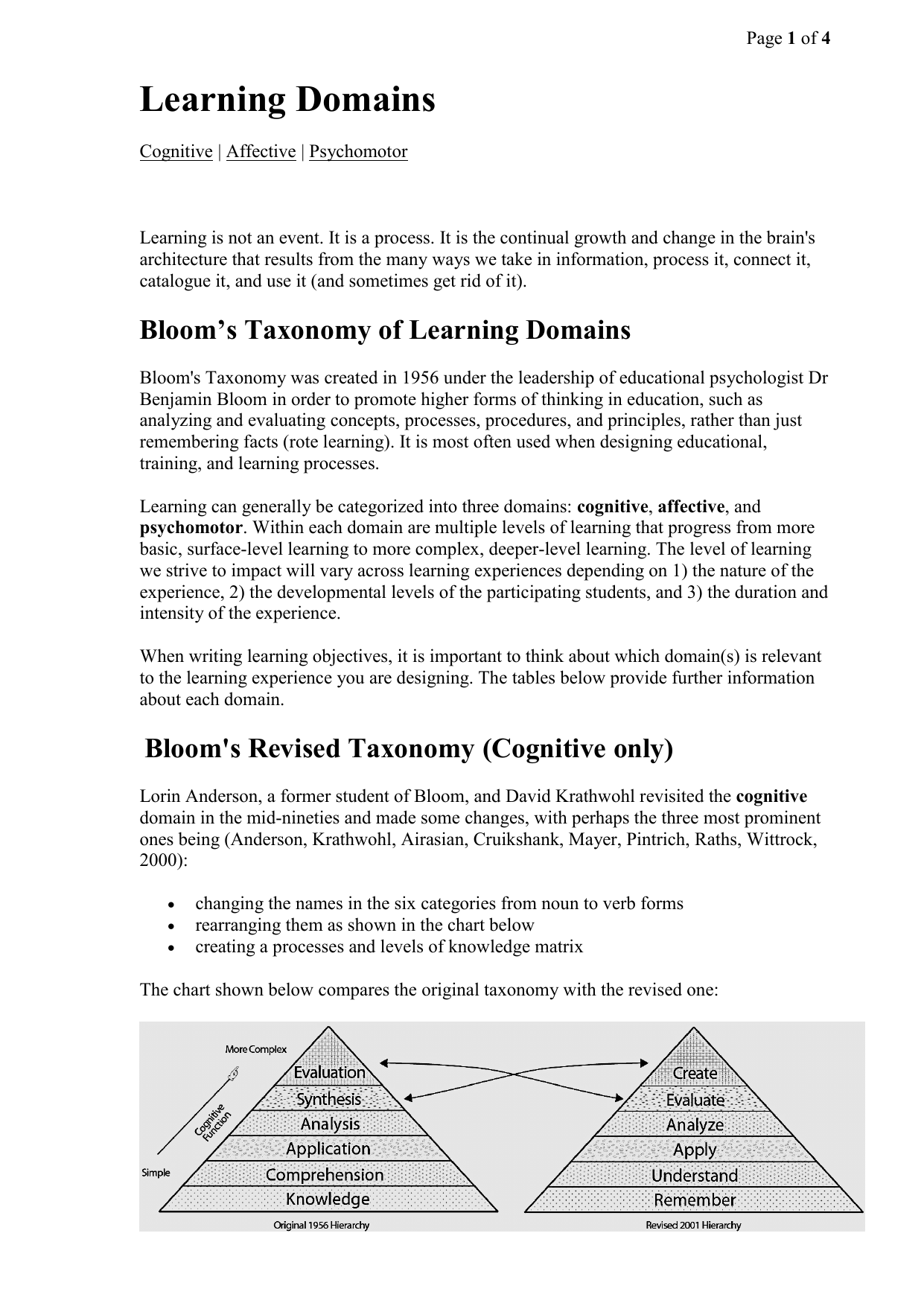
The cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum learning objectives. It is most often used when designing educational training and learning processes.
 Bloom S Taxonomy Learning Domains
Bloom S Taxonomy Learning Domains
There are three taxonomies.

What educational leader created a taxonomy of learning. In 1956 Benjamin Bloom created Blooms Taxonomy. Few educational theorists or researchers have had. Its Benjamin Bloom the man whose analysis of the increasing depths of learning gave us Blooms Taxonomy.
The SOLO Taxonomy was devised by Biggs and Collis in 1982 as an alternative to Blooms Cognitive Domain Taxonomy. Blooms Taxonomy was created in 1956 by educational psychologist Dr. Blooms Taxonomy Tables 1-3 uses a multi-tiered scale to express the level of expertise required to achieve each measurable student outcome.
Their framework soon became known as Blooms Taxonomy and provides a way of categorizing educational goals. If there is no change there is no learning. Blooms taxonomy engendered a way to align educational goals curricula and assessments that are used in schools and it structured the breadth and depth of the instructional activities and curriculum that teachers provide for students.
Bloom held a role on the Board of Examinations at the University of Chicago and wanted to create a test bank of items specifically designed to measure certain educational objectives Krathwohl 2002. The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive affective and sensory domains. In 1956 Benjamin Bloom with collaborators Max Englehart Edward Furst Walter Hill and David Krathwohl published a framework for categorizing educational goals.
Finks Taxonomy is known as the Taxonomy of Significant Learning In his book Creating Significant Learning Experiences Dee Fink defined learning in terms of change. Familiarly known as Blooms Taxonomy this framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching. This method was created in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education.
SOLO Structure of Observed Learning Outcomes Taxonomy is a systematic way of describing how a learners understanding develops from simple to complex when learning different subjects or tasks. Such forms include analyzing and evaluating concepts processes procedures and principles rather than just remembering facts. Blooms Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education such as analyzing and evaluating rather than just remembering facts.
In 1956 Benjamin Bloom and his team of collaborators published their book Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Blooms taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity.
Organizing measurable student outcomes in this way will allow us to select appropriate classroom assessment techniques for the course. Since then it is regarded as a comprehensive platform where the learning objectives and its outcomes are classified in a systematic way. Blooms Taxonomy of Learning Domains Blooms Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education such as analyzing and evaluating concepts processes procedures and principles rather than just remembering facts rote learning.
Blooms taxonomy taxonomy of educational objectives developed in the 1950s by the American educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom which fostered a common vocabulary for thinking about learning goals. The taxonomy was proposed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom an educational psychologist at the University of Chicago. Find read and cite all the research you.
PDF Students in computer science courses entering higher education begin with computer thinking and programming languages in a curricular unit CU. Effective leadership builds and promotes a positive organisational culture and professional learning community NQS Standard 72ACECQA recognising the important role of the educational leader and in response to sector feedback has developed The Educational Leader ResourceThis resource is a collection of practical advice resources case studies research reflections and references to. Our point is not to suggest that they are sacrosanct.
This model is used effectively for teaching and learning purposes. He believes in order for learning to occur there has to be some kind of change in the learner. Blooms Taxonomy is a classification of the different objectives and skills that educators set for their students learning objectives.
In the 1950s Benjamin Bloom and a group of collaborating psychologists created what is known as Blooms Taxonomy which is a framework for levels of understanding. One of the most well-known learning taxonomies is Blooms Taxonomy created in the 1950s by Benjamin Bloom Bloom 1956. Blooms Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education such as analyzing and evaluating concepts processes procedures and principles rather than just remembering facts rote learning.
Every discipline has some quibble with the specifics of these taxonomies.