X and consider using the techniques suggested by Theory Y. Theory X and Y of Human motivation was developed in the 1960s by Douglas McGregor an American social psychologist.
 Mcgregor S Theory X And Theory Y Of Motivation By The Enterprise World Magazine The Enterprise Diary Medium
Mcgregor S Theory X And Theory Y Of Motivation By The Enterprise World Magazine The Enterprise Diary Medium
What might be less immediately understandable are the differing effects of Theory X and Y on resulting behavior and productivity.
Douglas mcgregor theory x and y. It is to McGregors thorough research and curiosity in behavior and incentive that we owe our current understanding of Theory X and Theory Y. Douglas McGregor put forward a theory of motivation called as theory X and theory Y. Douglas McGregor has presented two opposite sets of assumptions about employees.
Understanding Theory X and Theory Y. Theory into practice Abraham Maslow viewed McGregor as a mentor. Based on the premises concerning human behaviour Prof.
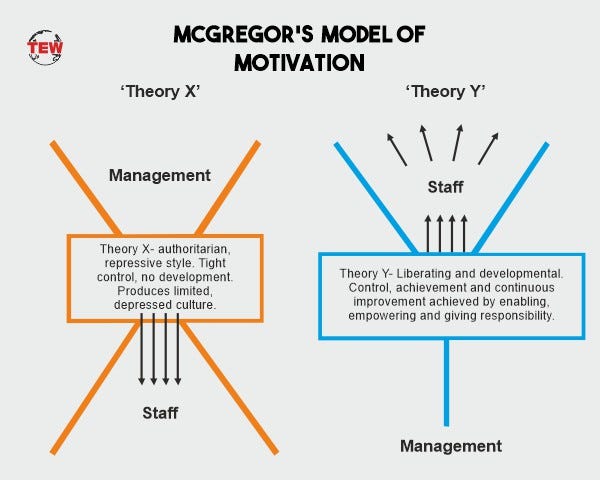
In his 1960 management book The Human Side of Enterprise Douglas McGregor made his mark on the history of organizational management and motivational psychology when he proposed the two theories by which managers perceive employee motivationHe referred to these opposing motivational methods as Theory X and Theory Y management. External motivation Includes the forces which exist inside the individuals as well as the controlled by the manager including items such as salaries working conditions company policy and job content items such as recognition. I The average person dislikes work and whenever possible will avoid it ii Most people are not ambitious have little desire for responsibility and prefer to be directed.
McGregors work was rooted in motivation theory alongside the works of Abraham Maslow who created the hierarchy of needsThe two theories proposed by McGregor describe. Toward a Construct-Valid Measure. However he found that an organisation.
It is something that makes people act or behave in a particular manner. Theory X and Theory Y of Motivation by McGregors. He was a strong supporter of Theories X and Y and he put Theory Y that people want to work achieve and take responsibility into practice in a Californian electronics factory.
McGregors Theory X and Y. Theory X is management style where the emphasis is on productivityon the concept of a fair days work on the evils of feather-bedding and targeted outputTheory Y is almost in complete contrast to that of Theory X. Douglas McGregors Theory X and Theory Y.
How do Theory X and Theory Y affect work output. Theory X and Theory Y was an idea devised by Douglas McGregor in his 1960 book The Human Side of Enterprise. Theory X and Theory Y introduced in the book and are known for management and human.
In the 1960s Douglas Murray McGregor a famous MIT professor of management wrote a book named The Human Side of Enterprise in which he analyzed the various behaviors of professionals at work. The Theory X and Theory Y created by Douglas McGregor in 1950s and developed later in the 1960s. Theory X and Theory Y were first explained by McGregor in his book The Human Side of Enterprise and they refer to two styles of management authoritarian Theory X and participative Theory YIf you believe that your team members dislike their work and have little motivation then according to McGregor youll likely use an authoritarian style of.
Jika manajemennya yakin bahwa sebagian dari karyawannya tidak menyukai pekerjaannya maka gaya manajemen akan cenderung ke gaya manajemen otoriter. This theory was first introduced in his book The Human Side of Enterprise It generally highlights two different management styles such as Authoritarian Theory X Participative Theory Y McGregors Theory X and Theory Y is a theory. The idea that a managers attitude has an impact on employee motivation was originally proposed by Douglas McGregor a management professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology during the 1950s and 1960sIn his 1960 book The Human Side of Enterprise McGregor proposed two theories by which managers perceive and address employee motivation.
According to McGregor the perception of managers on the nature of. Theory Y make assumptions that people in the work force. There are two theories ie.
They were created by Douglas McGregor while he was working at the MIT Sloan School of Management in the 1950s and developed further in the 1960s. Douglas McGregors Theory X and Y. One of which is negative called as Theory X and the other is positive so called as Theory Y.
Douglas McGregor 1906 1964 was a famous management professor in the field of personal development and motivational theory. The major distinct disadvantage of Theory X and Theory Y is that they are put forward as challenging sets of assumptions a supervisor is either motivated by Theory X or by Theory Y. What is X-Y Theory of Management.
Although nearly 50 years have passed since McGregors initial formulation of Theory X and Theory Y the substantive. He is best known for his development of the Theory X and Theory Y a leadership theory on two different leadership styles. In 1960 Douglas McGregor formulated Theory X and Theory Y suggesting two aspects of human behaviour at work or in other words two different views of individuals employees.
These have been represented by Theory X and Theory Y. Theory X and Theory Y. Theory X and Theory Y are theories of human work motivation and management.
Theory X is a conventional approach to motivation based on negative assumptions. Teori X dan Teori Y menurut Douglas McGregor Gaya manajemen suatu perusahaan sangat dipengaruhi oleh keyakinan dan asumsi manajemennya terhadap apa yang merupakan dorongan kerja karyawannya. However modern revisions including contingency theorists argue that Theory Y is not essentially a progressive alternative to a dull Theory X.
Business Management Leadership No Result. Douglas McGregor an American social psychologist proposed his famous X-Y theory in his 1960 book The Human Side Of EnterpriseTheory X and Theory Y are still referred to commonly in the field of management and motivation and whilst more recent studies have questioned the rigidity of the model Mcgregors X-Y Theory remains a valid basic principle from.
Moreover the demethylation of the paternal genome is much faster than that of the maternal genome and by the end of the zygotic stage the genome-wide methylation level in male pronuclei is already lower. The DNA methylation landscape of human early embryos DNA methylation is a crucial element in the epigenetic regulation of mammalian embryonic developmentWe show that the major wave of genome-wide demethylation is complete at the 2-cell stage contrary to previous observations in mice.
 Theories Of Development Ppt Video Online Download
Theories Of Development Ppt Video Online Download
Epigenetics isthe study of how the environmentand other factors can change the way that genesare expressed.
Epigenetic theory of development. Epigenetic theory builds on Ethnology which is the study of behavior as it relates to the evolution survival of a species. Development before birth including gametogenesis embryogenesis and fetal development is the process of body development from the gametes are formed to eventually combine into a zygote to when the fully developed organism exits the uterusEpigenetic processes are vital to fetal development due to the need to differentiate from a single cell to a variety of cell types that are arranged in. In medical practise however a.
Psychoanalyst Erik Eriksons stages of psychosocial development theorize a model of human psychological growth made up of eight stages that cover the entire lifespan from birth to old age. Epigenetic concept requires if consistently applied to organisms whose early development takes place within a womb a transmission of information via the specific maternal environment created. Epigenetics meanwhile means very different things to different researchers.
15 The causal mechanisms involved in the relationships between epigenetic marks how the brain develops and functions. Epigenetic psychobiological systems perspective is an emergent theory that views development as a product of interaction between biological and environmental forces. Erik EriksonJ Theory ofldentity Development Erik Erikson 1902-1994 the developmental sequence of the well-known eight stages of man.
The traits that are most useful will become more frequent within individuals making the survival of the species more likely. Thus he called it the Ego Psychology for it enables to identify it in each stage the life of a person. Movement upward along the diagonal axis represents normal development and shows the successive differen-tiation of the original undifferentiated structure and thus represents increasingly more ma-.
Epigenetic theory is a principle expounded on by psychologist Erik Erikson that claims that personality develops in eight predetermined stages. From a biological point of view this information is equal to genetic and cyto-plasmic information. Large parts of epigenetic research in particular in medical epigenetics consist of studies on correlations not causation.
The increased knowledge of epigenetics combined with rise of technologies such as CRISPRCas9 gene editing and next-generation sequencing in recent years allows us to better understand the interplay between epigenetic change gene regulation and human diseases and will lead to the development of new approaches for molecular diagnosis and. Other studies examine the involvement of epigenetic factors in gene regulation processes with the genome as first cause. Each stage is defined by a central crisis that the individual must grapple with to move on to the next stage.
Ones family upbringing builds up on these stages. While epigenetic changes do not alter the sequence of a persons genetic code they can. Eriksons theory outlined eight stages of personality development arguing that each stage depended on.
This theory is known as the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease DOHaD in which epigenetic memories involving DNA. But during the past 50 years the meaning of the term epigenetics has itself undergone an evolution that parallels our dramatically increased knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes. 2 Epigenetic regulation in the brain can also influence a variety of complex neural functions such as memory formation learning and the calibration of stress response circuitry.
These environmental factors during early childhood and adolescence can cause changes in expression of genes conferring risk of mental health and chronic physical conditions. This theory draws heavily upon some of Sigmund Freuds theories concerning the superego ego and id. AN EPIGENETIC THEORY OF EMOTIONS IN EARLY DEVELOPMENT 317 Freudian instinct theory and object-relations development theory are based on the proposition that critical periods are defined more saliently when epigenetic elements of the subject are considered along with corresponding social responses of the environment.
PS An aspect of evolution in which over generations genes for. In the Epigenetics theory as explained by Erikson he believed that childhood is very important in ones Stages of Personal Growth. A number of epidemiological studies have suggested that environmental stresses such as malnutrition during the fetal period can induce development of metabolic disorders such as obesity type 2 diabetes and hypertension and psychiatric disorders in later life.
The history of epigenetics is linked with the study of evolution and development. For example how tall they could eventually become or the kind of temperament they could have. It includes both the genetic.
Recent studies have provided insights into epigenetic regulation of developmental pathways in response to a range of external environmental factors Dolinoy Weidman Jirtle 2007. Brain development in mammals requires a precisely coordinated sequence of gene regulation events some of which are epigenetic in order to produce and spatially locate neurons and glial cells. The genes children inherit from their biological parents provide information that guides their development.
Epigenetics explains how early experiences can have lifelong impacts.
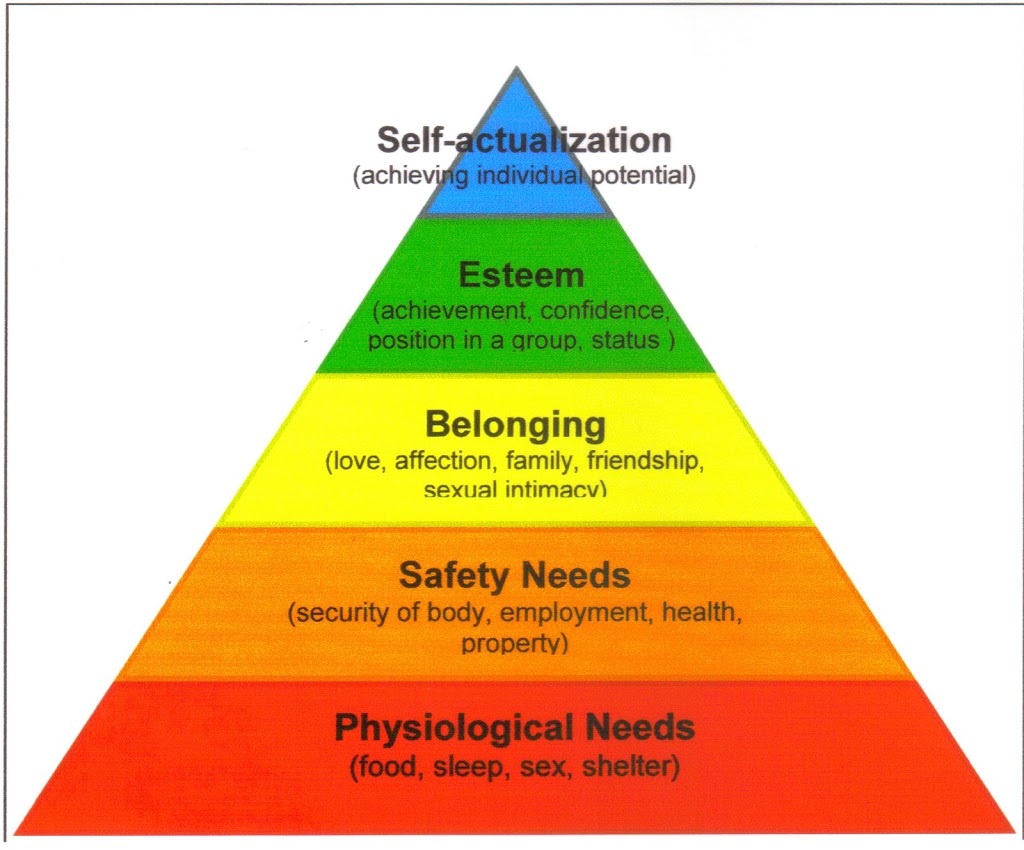
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs. The Five Basic needs from bottom to top are.

This theory has four need based levels that all humans have the desire to fulfill.
Abraham hierarchy of needs theory. This slightly clunky phrase simply means that humans want to feel that they are fulfilling their potential and making the most of their abilities. Hierarchy of Needs Holistic-Dynamic Theory Maslows theory is focused on potential for self-actualization how individuals fulfill their potential and what motives them to meet their needs. Background of Maslows Hierarchy of Needs Maslows Hierarchy of Needs HON is a developmental psychology theory proposed by Maslow1943 Humanistic Science and Trancendent Experiences By.
The hierarchy of needs is a theory of psychologist Abraham Maslow. The hierarchy is diagramed as a pyramid starting at the bottom with basic needs that must be satisfied for an individual to be able to progress to addressing more secondary needs. Abraham Maslows Hierarchy of Human Needs Theory is well famous among those who are familiar with the topic of Motivation in Psychology.
April 1 1908 June 8 1970 was an American psychologist who was best known for creating Maslows hierarchy of needs a theory of psychological health predicated on fulfilling innate human needs in priority culminating in self-actualization. 1 Physiological needs 2 Safety needs 3 Love and belonging needs 4 Esteem and prestige needs 5 Self-actualization needs. In nursing specifically nurses follow the model by at the least ensuring that patients physiological and basic needs are met.
Maslow himself noted this criticism. This theory is a classical depiction of human motivation. The urgency of these needs varies.
There is little scientific basis to the idea. Maslows Hierarchy of Needs often represented as a pyramid with five levels of needs is a motivational theory in psychology that argues that while people aim to meet basic needs they seek to meet successively higher needs in the form of a pyramid. Abraham Harold Maslow ˈ m ae z l oʊ.
This website is intended to be a starting point and the main difference with other websites is the visual representation of the theory which I hope will help get to grips with the theory. Pada tingkatan ini sesungguhya mempunyai hubungan yang sagat erat denga proses pengembangan diri maupun potensi yang dimiliki oleh seseorang. Maslows hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper A theory of Human Motivation in Psychological Review.
Physiological food and clothing safety job security love and belonging needs friendship esteem and self-actualization. Hierarki kebutuhan Maslow adalah teori psikologi yang diperkenalkan oleh Abraham Maslow dalam makalahnya A Theory of Human Motivation di Psychological Review pada tahun 1943. Maslows hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology.
Ia beranggapan bahwa kebutuhan-kebutuhan di tingkat rendah harus terpenuhi atau paling tidak cukup terpenuhi terlebih dahulu sebelum kebutuhan-kebutuhan di tingkat lebih tinggi menjadi hal yang memotivasi. The Hierarchy of Needs model can essentially be applied to all sectors of healthcare. According to humanist psychologist Abraham Maslow our actions are motivated in order to achieve certain needs.
When those needs are met the focus can then advance to the next level for further holistic care. Hierarchy of Needs Abraham Maslow 1954 Definition. Maslows Hierarchy of Needs Theory.
Comprising a five-tier model of human needs often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. Self Actualization Needs Kebutuhan aktualisasi diri aktualisasi diri merupakan tingkatan tertinggi didalam diri manusia menurut Maslows Hierarchy of Needs. Physiological safety love esteem and self-actualization.
Maslow was a psychology professor at Alliant International University Brandeis University Brooklyn. Maslow first introduced his concept of a hierarchy of needs in his 1943 paper A Theory of Human Motivation and his subsequent book Motivation and Personality. This hierarchy suggests that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to other more advanced needs.
Abraham Maslow is well renowned for proposing the Hierarchy of Needs Theory in 1943. Maslows hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. Maslows hierarchy of needs is a theory by Abraham Maslow which puts forward that people are motivated by five basic categories of needs.
Maslows hierarchy of needs says that once humans have satisfied their ego and obtained self-esteem that their ultimate need is that of self-actualization. The lowest requirement in the hierarchy must be satisfied before moving to higher levels. Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans innate curiosity.
This theory is based on the assumption that there is a hierarchy of five needs within each individual. These five needs are as follows-. From the bottom of the hierarchy upwards the needs are.
Its not my intention to give full information or an extensive discussion on every theory. Abraham Maslow as a renowned researcher in the study of human needs and motivation came up with his famous hierarchy of needs theory with a proposal that people are motivated by five levels of needs namely.
His conception of the adolescent taskweaving internal tastes talents and values together with elements of ones life history and the demands of ones culture into a coherent identityhas had profound effects. Erikson was famous for coining the identity crisis.
While his theory was impacted by psychoanalyst Sigmund Freuds work Eriksons theory centered on psychosocial development rather than psychosexual development.

Critical analysis of erikson's theory. Gods Word reveals what man needs to know about himself. Erikson also believes as did Freud that personality has. Erik Erikson was an ego psychologist who developed one of the most popular and influential theories of development.
Key Elements of Eriksons TheoryErik Erikson believed that we develop in psychosocial stages versus psychosexual stages that Freud developed Santrock 2008 p23. Critical Analysis of Erik Erikson Psychosocial Theory of Development. Therefore it is fair to say that.
As such what Erikson did by adding stages beyond adolescence was opening the door to adult personality development and therefore changes later in life. He saw that development progressed in eight steps depending on how the contact between the individual s ability and the needs of the social culture was changed. Therefore it is fair to say thatErikson is a psychoanalytic theoristHowever Erikson does argue that social and cultural influences have a criticalrole in shaping human development and less significance should be placed on the roleof sexual urges.
Eriksons theory stresses our rational adaptive nature is much easier to accept. However he did not imply that the crisis was by any means catastrophic but that they represent crucial developments in which a decisive turn one way or another is unavoidable Stevens 1983. Erik Homburger Erikson a German-American developmental psychologist was best known for his theory of the psychological development of human beings.
However many have foundEriksons theory offers a useful framework for analyzing developmentalhistories. The stages are Integrity versus Despair Generatively versus Stagnation Intimacy versus Isolation Identity versus Identity Confusion Industry versus Inferiority Initiative versus Guilt Autonomy versus Shame and Doubt and Trust versus Mistrust Santrock 2011. The understanding of adolescence is based on two approaches of comprehending human behaviour by Erik Erikson and Anna Freud.
Sigelman and Shaffer 1992. Between infancy and 18 months of age babies struggle with trust versus mistrust. Veena Ilame DOI1022161ijelsbookVeenaIlamecritical ISBN978-81-947261-7-3.
8 Many people prefer Eriksons theory to Freuds because they do not believe that people are dominated by sexual instincts. Erikson a 20th-century psychologist and psychoanalyst formulated the eight-stage life cycle theory in 1959 on the supposition that the environment plays a critical role in self-awareness adjustment human development and identity. Erikson believed and concentrated on the dichotomy that is between personality formation and accomplishment of roles while Freud believed that psychological unsettling does influences that are connected with adolescence were biologically based and socially all inclusive.
Man is created in the image of God to live in relationship to Him. However Erikson does argue that social and cultural influences have a critical. However Erikson himself defined his theory as a framework only Erikson 19501993 a statement that one of his legacies the Erikson Institute still stresses today Erikson Institute nd.
The word psychosocial was Eriksons term that he derived from the words psychological meaning mind and social meaning relationship Chapman 2007. Eriksons Doctrine of Man Every major psychological theory includes a doctrine of man a particular view of the essence of human nature. He lived between 1902 and 1994 and had a son by the name Kai Erikson who was a noted American sociologist.
Generativity versus stagnation is the seventh of eight stages of Erik Eriksons theory of psychosocial development. The stages that make up his theory are as follows. For this reason Freuds theory Psychosexual and Eriksons theory is psychosocial Shaffer Kipp 2010.
The id the ego and the superego. The work and legacy of Erik Erikson are described in this brief outline of his career his theories and his impact on psychoanalysis psychology history and the broader culture. Psychologically generativity refers to making your mark on the world through creating or nurturing things that will outlast an individual.
The work and legacy of Erik Erikson are described in this brief outline of his career his theories and his impact on psychoanalysis psychology history and the broader culture. Critics of Eriksons theory say that his theory is more applicable to boysthan to girls and that more attention is paid to infancy and childhood than toadult life despite the claim to be a life-span theory. Erikson is a psychoanalytic theorist.
This stage takes place during during middle adulthood ages 40 to 65 yrs. Erikson also believes as did Freud that personality hasthree components. Critical Times Critical Theory Elizabeth Douvan PhD University of Michigan and The Fielding Institute ABSTRACT.
Philosopher Analysis Erik Erikson. What Erikson has produced is a sequence of critical periods in the human life cycle. Eriksons psychosocial model is very generalised and he himself.
Eriksons Theory of Psychosocial Development Erikson theorized that every person moves through eight stages or crises of psychosocial development from birth to death. Erik Erikson created a Psychosocial Theory that describes eight different lifespan stages that all people go through as they age. Psychologist Erik Erikson s theory of psychosocial development emphasized socio-cultural factors as compared to Freud s psychosexual developmental stage and it was known as very rich classical development theory in that it proposed the developmental after the adolescence.
The id the ego and the superego. Psychosocial development theory is an expansion of Sigmund Freuds original five stages of development.
Expectancy theory proposes that an individual will behave or act in a certain way because they are motivated to select a specific behavior over others due to what they expect the result of that selected behavior will be. As managers Expectancy Theory can help us to understand how individual team members make decisions about behavioral alternatives in the workplace.
Vroom realized that an employees performance is based on individual factors such as personality skills knowledge experience and abilities.

Explain the expectancy theory. What does the expectancy theory explain about employees. The effort will lead to a good performance appraisal. The organizational rewards will satisfy his or her personal goals.
This process begins in childhood and continues throughout a persons life. Abraham Maslow and Frederick Herzberg also researched the relation between peoples needs and the efforts they make. Better job performance will lead to organizational rewards such as an increase in salary or benefits.
Expectancy instrumentality and valence. Victor Vroom a sociologist and business school professor at the Yale School of Management created the Expectancy Theory in the 60s. Expectancy Theory Victor Vroom The expectancy theory says that individuals have different sets of goals and can be motivated if they have certain expectations.
Expectancy is the individuals belief that effort will lead to the intended performance goals. Putting in more effort will yield better job performance. The theory attempts to explain why individuals choose to follow certain courses of action in organizations particularly in decision-making and leadership.
This means that even if an employer provides all that is required for motivation and it works with the majority in the organization some employees will still feel demotivated. The expectancy theory is typically a management or business principle although it can be used for self-motivation. This theory is about choice it explains the processes that an individual undergoes to make choices.
Very simply the expectancy theory says that an employee will be motivated to exert a high level of effort when he or she believes that. Expectancy theory or Expectancy theory of motivation proposes an individual will behave or act in a certain way because they are motivated to select a specific behavior over other behaviors due to what they expect the result of that selected behavior will be. Vrooms Expectancy Theory is based on the assumption that an individuals behavior results from the choices made by him with respect to the alternative course of action which is related to the psychological events occurring simultaneously with the behavior.
In this context positive role models that have worked hard to improve their performance who are then rewarded for all this effort will increase motivation. Expectancy theory describes the extent to which an individual is likely to pursue a certain course of action motivational force which is in turn a function of expectancy a belief that increased effort will produce better performance x instrumentality a belief that better performance will lead to certain outcomes x valence a belief that the outcome will. Expectancy instrumentality and valence.
However at the core of the theory is the cognitive process of how an individual processes the different motivational elements. Expectancy theory has three components. This is done before making the ultimate choice.
In essence the motivation of the behavior selection is determined by the desirability of the outcome. Since it is an association between effort and performance its value can range between 0 and 1. Expectancy theory predicts that employees in an organization will be motivated when they believe that.
Effort performance and outcome. Think of motivation as a chain where each link represents a condition and the intersection of each link represent its components. Expectancy theory is based on the belief that effort produces performance and performance produces desirable outcomes.
A good appraisal will lead to organizational rewards. When it comes to business managers and executives within companies use this theory to motivate their employees. Vrooms expectancy theory assumes that behavior results from conscious choices among alternatives whose purpose it is to maximize pleasure and to minimize pain.
In 1964 Canadian professor of psychology Victor Vroom developed the Expectancy Theory. Expectancy Theory basically states that a person behaves the way they do because they are motivated to select that behavior ahead of others because of what they expect the result of that behavior to be. Traditionally Expectancy theory was most applicable where motivated employees needed the reward on offer.
The expectancy theory is based on perceptions. Expectancy Theory or VIE Theory is based on the premise that motivation occurs when three specific conditions are satisfied. Expectancy describes the persons belief that I can do this.
The Expectancy theory states that employees motivation is an outcome of how much an individual wants a reward Valence the assessment that the likelihood that the effort will lead to expected performance Expectancy and the belief that the performance will lead to reward Instrumentality. In it he studied peoples motivation and concluded it depends on three factors. Expectancy instrumentality and valence.
Expectancy is the probability that a particular action will lead to the outcome it is the perception in the mind of the individual of the likelihood that a particular action or behaviour will lead to a certain outcome.
